Essential Guide to the Low FODMAP Diet: Improve Digestive Health in 2025
The Low FODMAP Diet is a revolutionary approach specifically designed for individuals struggling with digestive disorders such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). It involves eliminating certain carbohydrates known as FODMAPs, which can trigger unpleasant symptoms like bloating, gas, and cramps. This comprehensive guide provides insights into low FODMAP foods, meal plans, and overall strategies to enhance your gut health and improve your wellbeing in the coming year.
Understanding FODMAPs and Their Impact on Digestive Health
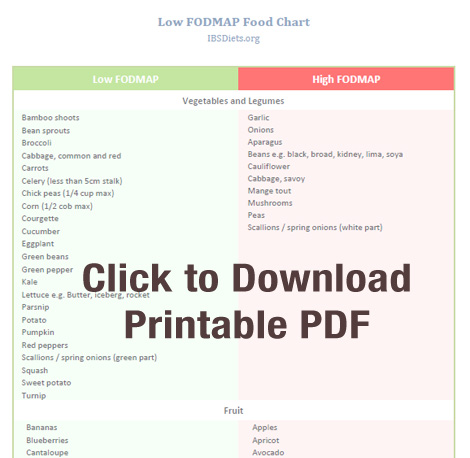
Understanding FODMAPs is crucial for anyone considering the **FODMAP diet**. FODMAP stands for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols. These are types of short-chain carbohydrates poorly absorbed in the small intestine. As a result, they can lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain and discomfort for individuals with **FODMAP intolerance**. By reducing or eliminating high FODMAP foods, many find relief from digestive distress and an improvement in overall gut health.
Common Trigger Foods to Eliminate
Identifying and eliminating **trigger foods** is the first step in following the low FODMAP diet. Common high FODMAP foods include certain fruits like apples and pears, legumes, dairy products containing lactose, and sweeteners like honey and agave syrup. Each person may have different sensitivities; therefore, keeping a **food diary for IBS** can help pinpoint specific triggers. Monitoring reactions to these foods allows individuals to customize their nutrition plans effectively.
The FODMAP Elimination Phase
The elimination phase typically lasts 4-6 weeks, during which you avoid high FODMAP foods entirely. This time frame allows your gut to heal and provides a clearer indication of which foods truly impact your symptoms. During this phase, it’s essential to focus on the variety of low FODMAP foods available, such as bananas, carrots, eggs, and various proteins. **Meal prepping** can assist in maintaining adherence to the diet, making it easier to access nutritious meals while avoiding high FODMAP options.
Low FODMAP Meal Planning: Practical Tips for Success
Planning meals in advance is key to success on a **low FODMAP lifestyle**. Developing a structured approach, including a **low FODMAP shopping list** and meal ideas, ensures that nutritious options are always available. Here are some practical tips for effective meal planning.
Creating a Low FODMAP Food List
A crucial step in transitioning to a low FODMAP diet is compiling a comprehensive **low FODMAP food list**. This list helps to ensure variety and nutritional balance while avoiding **FODMAP triggers**. Focus on incorporating whole foods such as leafy greens, certain meats, gluten-free grains, and lactose-free dairy. Generally, foods that are minimally processed are preferable, as they contain fewer additives that may cause adverse effects.
Low FODMAP Recipe Ideas
Finding tasty and satisfying **low FODMAP recipes** can make the diet more enjoyable. For a nourishing breakfast, consider a smoothie made with kale, almond milk, and banana. Lunch can consist of a quinoa salad loaded with peppers, cucumber, and grilled chicken. For dinner, low FODMAP options like a simple stir-fry using bok choy, carrots, and firm tofu provide nutritional benefits without discomfort.
Healthy Snacking on a Low FODMAP Diet
Inclusivity in meals doesn’t have to end with snacks. There are plenty of **low FODMAP snacks** options that maintain nutrient balance while satisfying cravings. Consider options like rice cakes topped with peanut butter or almond butter, carrot sticks with hummus made from allowed ingredients, or yogurt made from lactose-free dairy products for a quick and satisfying treat.
The Benefits of Following a Low FODMAP Diet
Many individuals report aspects of life vastly improved after starting a low FODMAP diet. Key **FODMAP diet benefits** include reduced bloating, less abdominal pain, and an overall sense of wellbeing. For those suffering from IBS, managing symptoms effectively can lead to a healthier, more active lifestyle.
Improved Gut Health
Through reducing fermentable carbs, the low FODMAP diet encourages a better environment for the **gut microbiome**. This is essential for digestion and nutrient absorption. Supporting **gut health** through this dietary approach not only alleviates symptoms but may also play a role in maintaining psychological health and comfort.
Supporting Ongoing Wellness
Following a low FODMAP diet can lead to weight management and other health improvements as individuals become more conscious of their dietary choices. Ultimately, prioritizing **nutritional balance** while enjoying **gut-friendly meals** underscores the potential success of the low FODMAP diet as a comprehensive approach to wellness.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The low FODMAP diet can be a game-changing strategy for individuals seeking relief from digestive distress. It offers an opportunity to understand and improve digestive health profoundly. The path may seem daunting; however, by following established protocols, utilizing helpful resources, and customizing an eating plan that caters to personal sensitivities, success is within reach. As you embark on this journey, make sure to regularly review resources, consider consulting with a **dietitian**, and remain mindful of how various foods impact your gut health.
FAQ
1. What is a low FODMAP diet, and who can benefit from it?
The low FODMAP diet is a dietary approach tailored for those who experience digestive issues, particularly IBS. By reducing specific carbohydrate groups that may cause discomfort, it helps alleviate symptoms and improve gut health. Many who suffer from food intolerances find substantial relief through this diet.
2. How do I know which foods to avoid?
Identifying high FODMAP foods usually involves consulting a **FODMAP food chart** and tracking personal reactions to various foods. Utilizing resources such as mobile apps or working with a certified dietitian can help to construct a personalized list of foods to eliminate.
3. Can I follow the low FODMAP diet long-term?
While some individuals may benefit from long-term adherence, it’s typically suggested to reintroduce foods methodically after the elimination phase to develop a customized diet plan that includes manageable doses of FODMAPs. This can enhance overall nutrition and satisfaction.
4. Are there effective strategies for dining out on a low FODMAP diet?
Dining out can pose challenges on a low FODMAP diet. However, knowing how to communicate dietary needs to restaurant staff and selecting dishes with accessible ingredients can make navigating menus easier. Don’t hesitate to ask for modifications to suit your dietary requirements.
5. What supplements should I consider while following a low FODMAP diet?
Some individuals may benefit from **low FODMAP supplements**, such as probiotics, to support gut health and aid digestion. It’s important to choose probiotics designed for digestive comfort and consult a healthcare professional before starting new supplements.