“`html
Coyote Diet: Effective Ways to Improve Your Knowledge About Coyote Feeding Habits in 2025
Understanding Coyote Feeding Ecology
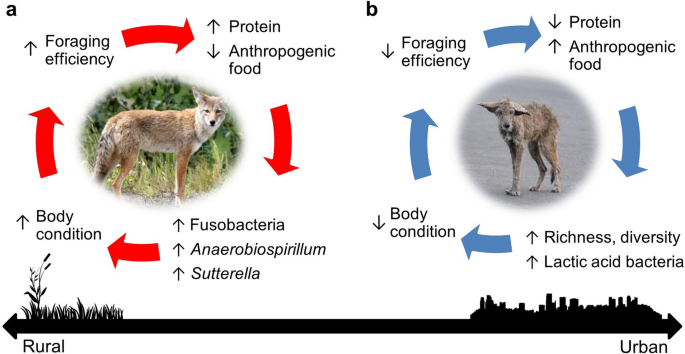
To effectively grasp coyote diet patterns, it’s essential to understand their feeding ecology. This encompasses how they interact with their environment, the types of prey they seek out, and their general food choices. Coyotes exhibit an omnivorous nature, meaning they consume both plant and animal matter. Their adaptability allows them to exploit various food sources based on availability, which changes seasonally. For instance, in urban areas, coyotes might scavenge from human waste, while in rural settings, their prey availability includes small mammals and birds. By studying the dietary preferences of coyotes, researchers can better understand their role in the ecosystem.
Coyote Seasonal Diet
The seasonal diet of coyotes can vary greatly depending on environmental changes. During the spring and summer, they often consume a higher quantity of small mammals such as rabbits and rodents, which are abundant during these warmer months. Conversely, winter can limit their food sources, leading them to adapt by scavenging on carrion or hunting in packs for larger prey. Observing these seasonal changes is critical for conservation efforts, as it informs wildlife management strategies tailored to their fluctuating needs.
Coyote Foraging Strategies
Coyotes are known for their versatile foraging strategies, showcasing remarkable adaptability in hunting and scavenging techniques. They employ several hunting styles, including solo hunting, pack behavior, and even collaborative strategies during feeding. This flexibility allows them to thrive in various habitats, from deserts to urban areas. By understanding these behaviors, one can appreciate how coyote adaptations contribute to their success as predators.
The Impact of Prey Availability on Coyote Diet
Coyotes’ diets are profoundly influenced by the availability of prey. Changes in local ecosystems, such as habitat loss or urban development, can restrict food sources, leading to shifts in coyote eating patterns. For instance, studies have shown that in heavily urbanized regions, coyotes might show preferences for alternative food sources, including human-generated waste, which might not have been their primary choice in less disturbed areas. This d dietary adaptability is key in ensuring their survival and maintaining ecological balance.
Coyote Hunting Techniques and Behavior
Coyote hunting involves a set of sophisticated techniques honed over generations. Their hunting strategies vary greatly based on prey type and environmental conditions, thereby affecting their predation rates. Coyotes are agile and opportunistic hunters, capitalizing on their surroundings to improve their hunting success. Understanding their behaviors during hunts gives insight into their social feeding behavior, especially when they hunt and share food as a family.
Coyote Scavenging Behavior
Coyotes are also adept at scavenging, which plays a crucial role in their feeding ecology. They will often take advantage of remains left by other predators or road-killed animals to supplement their diet. This scavenging behavior not only helps them in times of food scarcity but also contributes to the ecosystem balance, aiding in the natural process of recycling nutrients.
Coyote Competition for Food
Competition for food can significantly influence coyote populations. In various ecosystems, coyotes compete with other wildlife, including other carnivores, which can affect their dietary choices. For instance, they might shift their hunting focus to less competitive prey or utilize prey that are more abundant in their habitat. This behavior illustrates the importance of managing both coyote populations and other predatory species to maintain healthy ecological systems.
Coyote Nutrition and Health
A proper understanding of a coyote’s nutritional requirements is vital in determining their health and reproduction levels. A balanced diet rich in proteins, fats, and essential nutrients is necessary, particularly during breeding seasons. The nutritional value of prey directly impacts coyote populations, affecting aspects such as weight gain and overall vitality. As such, it is imperative to consider food source quality when assessing coyote populations and their health.
The Role of Coyotes in the Ecosystem
Coyotes play an integral role in maintaining the ecological balance within their habitats, influencing small mammal populations and contributing to a healthy ecosystem. Their actions shape food web dynamics, regulate prey populations, and even help in nutrient cycling through their kills and scat. Understanding the broader implications of their diet diversity is essential for appreciating their impact on an ecosystem.
Coyote Diet and Reproduction
Research has shown that a coyote’s diet can directly affect its reproductive success. Adequate nutrition leads to healthier litters, with enough resources available to nurture young coyotes. Seasonal shifts in prey can drastically shape the reproductive outcomes. When food is scarce, cub growth and survival rates can plummet, highlighting the interconnectedness of diet and population sustainability.
Coyotes and Human Interactions
As urban areas expand, the interactions between coyotes and humans become more common. This can lead to misconceptions regarding their diet and behavior. It’s crucial to educate the public on their urban feeding habits and to develop strategies for coexistence that can help mitigate conflict. Promoting awareness on coyote adaptability and role as scavengers can foster a better understanding of their ecological significance in urban settings.
Monitoring Coyote Populations
With advancements in wildlife research, monitoring coyote populations and their dietary choices has become more sophisticated. Technology, such as GPS tracking and camera traps, allows researchers to study coyote movement, habitat use, and their interaction with various prey species. By utilizing these methods, we can uncover valuable insights into their feeding ecology and inform wildlife management practices effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Coyotes utilize a diverse diet influenced by seasonal changes and prey availability.
- Their hunting techniques and scavenging behavior help maintain the ecosystem balance.
- Understanding their interactions with humans is important for coexistence.
- Research advancements are crucial for monitoring and managing coyote populations.
FAQ
1. What are the primary components of a coyote’s diet?
Coyotes primarily consume small mammals, birds, fruits, and occasional carrion. Their diet reflects their omnivorous nature, adapting to available food sources in their environment, whether urban or rural.
2. How does the urban environment affect coyote diet?
In urban areas, coyotes often adapt by scavenging human food waste and hunting domestic animals. This alteration reflects their dietary adaptability, showcasing their ability to thrive in changing environments.
3. What impact do coyotes have on local ecosystems?
Coyotes play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, controlling prey populations, and influencing biodiversity. Their presence can help regulate populations of small mammals, contributing to overall ecosystem health.
4. How do seasonal changes influence coyote feeding habits?
Seasonal changes affect food availability, pushing coyotes to adapt their diets according to what is abundantly available. For example, they may rely more heavily on rodents in warmer months and switch to scavenging in winter.
5. What research exists on coyote nutrition and health?
Numerous studies focus on the nutritional needs of coyotes, highlighting how diet impacts their reproductive success, weight gain, and overall health. These insights contribute to effective wildlife management strategies that ensure predator populations remain healthy.
6. How does coyote feeding behavior change in competition with other predators?
When faced with competition, coyotes might alter their hunting patterns, seeking less competitive prey or moving to areas with abundant food. This adaptability aids their survival and influences local predator dynamics.
7. What strategies can help people coexist with coyotes?
Education about coyote behavior and implementing measures such as securing trash, not feeding wildlife, and understanding their ecological role can help foster coexistence and reduce conflicts between humans and coyotes.

“`
